Evaporative Cooling Pad Analysis

1. Structure and Working Principle
Paper evaporative cooling pads usually adopt a 45°×15° cross-angle corrugated structure, with 45° grooves tilted downward toward the outer surface of the wet curtain pad. This design helps to keep most of the water on the outer surface of the pad, while the inner surface remains wet but basically no water flows through, forming a stable water film.
Water Film Distribution
The corrugated structure of the paper pad makes the water evenly distributed on the outer surface, and the inner surface only remains wet, avoiding the loss of efficiency caused by water flowing through the surface. This design ensures full contact between air and water film and improves evaporation efficiency.
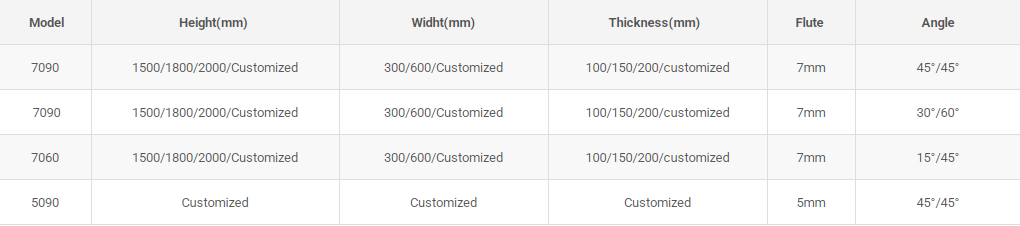
2. Performance Characteristics
Water Holding Capacity
Paper pads have a high water holding capacity and can absorb and hold relatively large amounts of water. When wet, paper pads can hold more water than plastic pads, providing a longer-lasting cooling effect under the same conditions.
Drying Speed
Paper pads dry slowly, and usually take 30 minutes or more to dry completely when wet. This characteristic enables the paper pad to provide a more stable cooling effect when controlled by a timer, avoiding cooling interruptions caused by rapid drying.
3. Application scenarios and advantages
Water quality adaptability
Paper pads are suitable for places with good water quality, because poor water quality may cause the paper pad to be easily blocked or moldy, affecting the service life and cooling effect.
Cooling effect
Paper pads can provide efficient cooling effect in dry environments, especially for places that require long-term stable cooling, such as industrial plants, agricultural greenhouses, etc.
Economical
Paper pads have a low cost and are suitable for projects with limited budgets. However, their service life is relatively short, usually 3 to 5 years, and they need to be replaced regularly.

4. Comparison with plastic pads
Corrugated structure
Paper pads have smaller corrugations and more uniform water film distribution; plastic pads have larger corrugations and high water flow requirements, but may cause water droplets to gather and increase wet garbage on the ground.
Water holding and drying characteristics
Paper pads have strong water holding capacity and dry slowly; plastic pads have weak water holding capacity and dry quickly. This difference makes paper pads more advantageous when controlled by a timer.
Static pressure and cooling effect
The static pressure of paper pads is easily increased due to dirt, which reduces the air speed; the dirt of plastic pads has little effect on the static pressure, but dirt accumulation should be avoided.
5. Precautions for use
Regular cleaning
Paper pads are easily affected by dirt and minerals, and need to be cleaned and dried regularly to prevent mildew and clogging.
Water quality management
Avoid using water sources containing a large amount of impurities to extend the service life of paper pads.
Replacement cycle
The service life of paper pads is generally 3 to 5 years, and they need to be replaced in time according to actual use.

